The Action Potential: Images
These following images should help you to see how the action potential
moves along the axon's membrane. Take a look at the animated
figure (16 k) which includes these imagese in motion (it may not work
on all web browsers) .
|
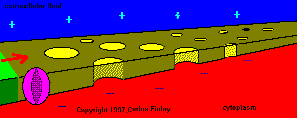
At rest, the inside of the neuron is slightly negative due to a higher
concentration of positively charged sodium ions outside the neuron.
|
|
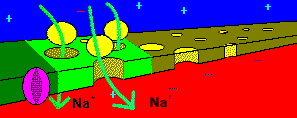
When stimulated past threshold, sodium channels open and sodium rushes
into the axon, causing a region of positive charge within the axon.
|
|
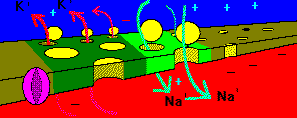
The region of positive charge causes nearby sodium channels to open.
Just after the sodium channels close, the potassium channels open wide,
and potassium exits the axon.
|
|
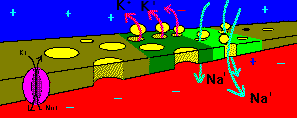
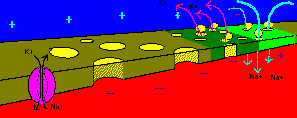
This process continues as a chain-reaction along the axon. The
influx of sodium depolarizes the axon, and the ourflow of potassium repolarizes
the axon.
|
|
The sodium/potassium pump restores the resting concentrations of sodium
and potassium ions
|
|




